1998 was a pivotal year that introduced innovations still shaping our lives today. From breakthroughs in technology to advancements in healthcare, the inventions of this year laid the groundwork for future progress we now take for granted.
We saw the emergence of gadgets that revolutionized how we communicate and manage our daily tasks. These top inventions not only showcased remarkable creativity but also set trends that influenced various industries for years to come.
Join us as we delve into the most impactful creations from 1998, celebrating the ideas that have driven our modern world forward and continue to inspire ongoing innovation.
1. Emergence of Advanced Search Engine Technology
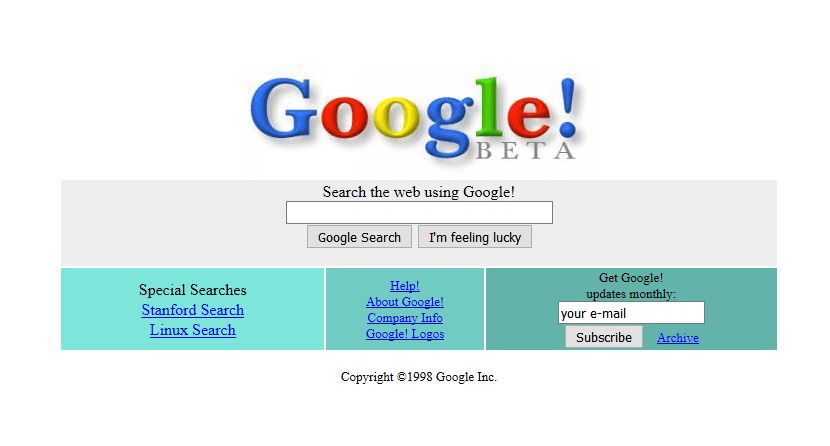
In 1998, significant advancements in search engine technology reshaped how we access information online.
Revolutionizing Information Retrieval
- Founded by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google introduced the groundbreaking PageRank algorithm that enhanced search result relevance and accuracy.
- Implemented a system that ranked web pages based on backlink quality and quantity, setting new standards for search engines.
- Transformed user experience by delivering more precise and reliable search results, making information retrieval faster and easier.
- Published by the W3C, XML (Extensible Markup Language) provided a flexible framework for creating standardized data formats.
- Enabled seamless data sharing across diverse platforms and applications, improving interoperability on the web.
- Facilitated the development of more user-friendly and accessible websites, broadening internet accessibility for millions worldwide.
2. Introduction of the Digital Video Disc (DVD)

The Digital Video Disc (DVD) began revolutionizing how we watch movies in the late ’90s. By 1998, DVDs were steadily replacing traditional formats.
Transition from VHS to DVD
We saw DVDs gain momentum as they offered superior video and audio quality compared to VHS tapes. Higher storage capacity allowed us to enjoy longer films and additional content. Convenience also played a role, with random access enabling us to jump to specific scenes effortlessly. These advantages made DVDs increasingly popular among consumers.
Impact on Media Consumption
DVDs transformed our media consumption by providing a more reliable and durable format. Unlike VHS tapes, DVDs didn’t degrade with each playback, ensuring consistent quality. The enhanced features, such as interactive menus and bonus materials, enriched our viewing experience. This shift not only improved how we watched movies but also set new standards for home entertainment.
3. Advancements in Computer Hardware
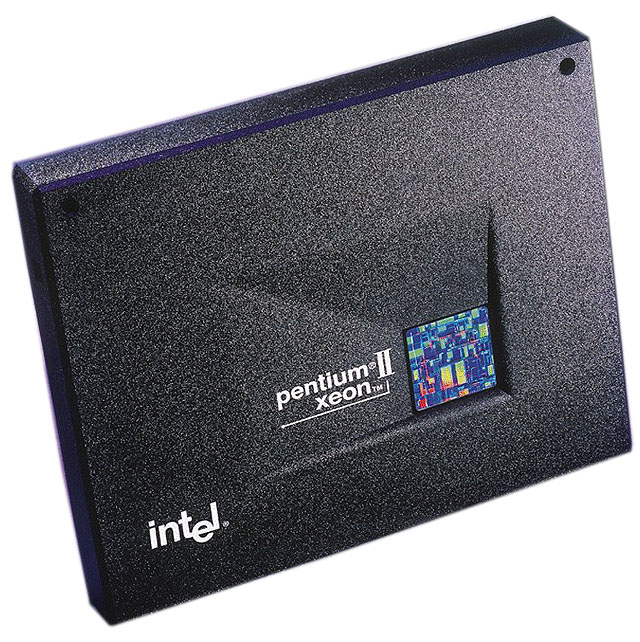

In 1998, computer hardware experienced remarkable advancements that boosted performance and reshaped personal computing.
Development of New Processor Technologies
We saw significant progress in processor technologies this year. Intel launched the first Xeon processors in June, introducing the Pentium II Xeon with impressive specifications:
| Processor | Manufacturer | Launch Date | Clock Speed(s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Celeron (Covington) | Intel | April 15, 1998 | 266 MHz, 300 MHz | First Celeron processors without L2 cache |
| Intel Pentium II Xeon | Intel | June 29, 1998 | 400 MHz, 450 MHz | Designed for servers and workstations |
| AMD K6-2 | AMD | May 28, 1998 | 266 MHz to 550 MHz | Introduced 3DNow! SIMD technology |
| Cyrix MII | Cyrix | May 1998 | 233 MHz to 300 MHz | Used PR rating to compare performance |
| IDT WinChip 2 | IDT | 1998 | 200 MHz to 266 MHz | Affordable x86 processor with 3DNow! support |
Simultaneously, AMD introduced its K62 processor line in May, offering speeds ranging from 266 MHz to 550 MHz and bus speeds between 66 MHz and 100 MHz. The K62, an enhanced version of AMD’s K6 processor, provided better performance and helped AMD regain competitiveness in the market.
Evolution of Personal Computing Systems
Apple transformed personal computing with the launch of the iMac in August 1998. This all-in-one desktop combined a sleek design with powerful features, including USB connectivity and enhanced graphics. The iMac not only improved user experience but also played a vital role in Apple’s financial turnaround, setting new standards for aesthetic and functional personal computers.
4. Breakthroughs in Mobile Communications
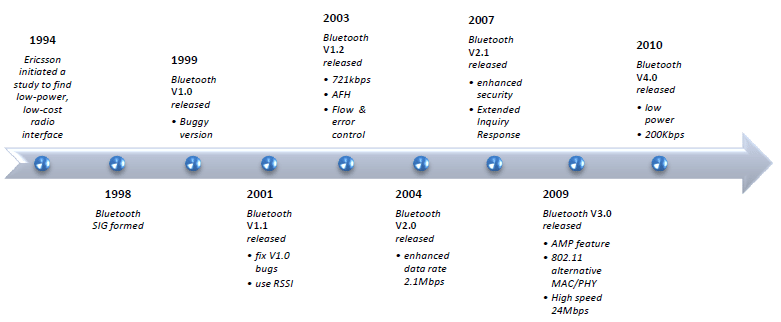
Introduction of Bluetooth Standards
In 1998, we saw the foundational work for Bluetooth technology take shape. Although Bluetooth 1.0 launched a year later, the late ’90s set the stage for seamless wireless connections, enabling devices like headsets and keyboards to communicate effortlessly. This breakthrough paved the way for the interconnected mobile ecosystems we rely on today.
Early Developments in Smartphone Technology
While smartphones as we know them didn’t exist in 1998, significant advancements were underway. Internet and web access surged, with e-commerce giants like Amazon and eBay expanding rapidly. These developments influenced the future of mobile devices, integrating robust online capabilities that would later become standard features in modern smartphones.
5. Innovations in Multimedia Formats

In 1998, groundbreaking advancements in multimedia formats reshaped how we consume and share digital content.
Rise of the MP3 Audio Format
We witnessed the surge of the MP3 audio format, revolutionizing digital music. MP3s compressed audio files without significant quality loss, making them easier to store and share online. This innovation leveraged the expanding internet infrastructure, allowing users to download and distribute music effortlessly. The accessibility and convenience of MP3s set the stage for the digital music era, paving the way for platforms like Napster and future streaming services.
Transformation of the Music Industry
Our music industry underwent a significant transformation thanks to MP3s. Traditional distribution channels, such as physical CDs and cassette tapes, began to decline as digital downloads gained popularity. Artists and record labels adapted by embracing digital marketing and online distribution. This shift not only changed how music was consumed but also introduced new revenue models, including digital sales and advertising-based streaming. The ease of sharing MP3s also fostered greater music discovery and global reach, expanding audiences and influencing the creation of diverse musical genres.
6. Progress in Space Exploration and Astronomy

In 1998, significant strides were made in space exploration and astronomy, laying the groundwork for future discoveries and missions.
Launch of Key Space Missions
We witnessed the launch of several pivotal space missions in 1998.
| Date of Launch | Mission Name | Launch Vehicle | Launch Site | Purpose/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 7, 1998 | Lunar Prospector | Athena II | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, LC-46 | NASA lunar orbiter to map the Moon’s composition and search for possible polar ice deposits. |
| January 22, 1998 | STS-89 (Endeavour) | Space Shuttle Endeavour | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39A | Space Shuttle mission to Mir space station; delivered supplies and exchanged U.S. astronauts. |
| April 17, 1998 | STS-90 (Columbia) | Space Shuttle Columbia | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39B | Neurolab mission to study the effects of microgravity on the nervous system. |
| July 4, 1998 | Nozomi (Planet-B) | M-V rocket | Uchinoura Space Center, Japan | Japan’s first Mars probe aiming for Mars orbit insertion. |
| June 2, 1998 | STS-91 (Discovery) | Space Shuttle Discovery | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39A | Final Shuttle-Mir docking mission; concluded Phase One of the International Space Station program. |
| October 24, 1998 | Deep Space 1 | Delta II 7326 | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, SLC-17A | NASA mission to test advanced technologies including ion propulsion. |
| October 29, 1998 | STS-95 (Discovery) | Space Shuttle Discovery | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39B | Mission included astronaut John Glenn’s return to space at age 77; research mission in support of future space exploration. |
| November 20, 1998 | Zarya (FGB) | Proton-K rocket | Baikonur Cosmodrome, Site 81 | First module of the International Space Station (ISS). |
| December 4, 1998 | STS-88 (Endeavour) | Space Shuttle Endeavour | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39A | First Space Shuttle mission to assemble the ISS; delivered Unity module and connected it to Zarya module. |
| December 11, 1998 | Mars Climate Orbiter | Delta II 7425 | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, SLC-17A | NASA mission to study Martian climate, atmosphere, and surface changes. |
Technological Enhancements for Spacecraft
Advancements in spacecraft technology also marked 1998 as a landmark year. NASA’s Deep Space I, powered by an advanced ion drive, set out in October for a July 1999 encounter with an asteroid, showcasing the potential of ion propulsion for long-distance space travel. Meanwhile, the Mars Global Surveyor achieved its final orbit, beginning to create the most detailed maps of the Red Planet to date. These technological enhancements not only improved mission capabilities but also paved the way for more ambitious explorations in the years to come.
7. Medical and Biotechnological Advances
New Cancer Prevention and Treatment Therapies
In 1998, significant strides were made in the fight against cancer, particularly in the prevention of breast cancer. One of the most groundbreaking developments was the FDA’s approval of Tamoxifen for reducing the risk of developing breast cancer in high-risk women. This approval marked a historic moment—the first time a medication was sanctioned not just for treating cancer but for actively preventing it.
Tamoxifen’s Impact on Breast Cancer Prevention
-
Significant Risk Reduction: The approval was largely based on the results of the Breast Cancer Prevention Trial (BCPT). This landmark clinical trial demonstrated that Tamoxifen could reduce the incidence of invasive breast cancer by approximately 49% among women who were at increased risk. Essentially, Tamoxifen prevented nearly half of the expected breast cancer cases in the study group, offering a powerful preventive strategy.
-
Mechanism of Action: Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It works by binding to estrogen receptors in breast tissue, effectively blocking estrogen from promoting the growth of estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer cells. By inhibiting this pathway, Tamoxifen can prevent the initiation and progression of certain breast cancers.
-
FDA Approval for Risk Reduction: In October 1998, recognizing the profound implications of the BCPT results, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officially approved Tamoxifen for reducing the risk of breast cancer in high-risk women. This was a pivotal development in oncology, shifting the focus toward prevention.
Shifting the Paradigm with Chemoprevention
-
Introduction of Chemoprevention: Tamoxifen’s success ushered in a new era of chemoprevention, the use of drugs to prevent disease. This concept revolutionized cancer therapy by highlighting the potential of medications to stop cancer before it starts, rather than solely treating it after diagnosis.
-
Inspiring Further Research: The effectiveness of Tamoxifen spurred researchers to explore other potential preventive agents. It led to increased interest in identifying compounds that could serve similar roles in reducing cancer risk with possibly fewer side effects.
Subsequent Studies and Developments
-
Preventing Contralateral Breast Cancer: In May 1998, studies confirmed that Tamoxifen also reduced the incidence of cancer in the opposite breast (contralateral breast cancer) among women who had been previously treated for breast cancer. This finding emphasized Tamoxifen’s role not just in prevention but also in reducing recurrence.
-
The STAR Trial: Building on Tamoxifen’s achievements, the Study of Tamoxifen and Raloxifene (STAR) was launched in May 1999. This major clinical trial aimed to compare Tamoxifen with another SERM, Raloxifene, to determine which was more effective in preventing breast cancer with fewer adverse effects.
Challenges and Advances in Cancer Therapy Development
While Tamoxifen represented a triumph in cancer prevention, other avenues explored in 1998 highlighted the complexities of cancer therapy development:
- Angiogenesis Inhibitors: Researchers investigated angiogenesis inhibitors, drugs designed to starve tumors by blocking the formation of new blood vessels that supply them with nutrients. Although early studies in mice were promising, translating these results to human treatments proved challenging, underscoring the intricate nature of cancer biology.
Breakthroughs in Genetic Research
Advancements in genetic research during 1998 played a crucial role in shaping personalized medicine and targeted therapies:
-
Genetic Insights Fuel Targeted Therapies: The development of Tamoxifen as a targeted therapy was bolstered by a deep understanding of genetic factors and hormone receptor statuses in breast cancer. Recognizing that some breast cancers are driven by estrogen allowed for treatments specifically designed to interrupt that pathway.
-
Combating Viral Resistance in AIDS: The approval and refinement of combination therapies for AIDS, including protease inhibitors, highlighted the importance of genetic research in addressing viral mutations and resistance. These treatments significantly improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
The Importance of Genetics in Personalized Medicine
- Tailoring Treatments: The breakthroughs of 1998 emphasized the critical role of genetics in developing effective, personalized medical treatments. By focusing on individual genetic profiles and the specific mechanisms of diseases, therapies could be more precisely targeted, increasing their efficacy and reducing side effects.
The Legacy of 1998’s Medical Advances
The year 1998 stands as a landmark in medical history for its contributions to disease prevention and personalized medicine. The approval of Tamoxifen for breast cancer risk reduction not only provided hope to countless high-risk women but also set a new course for medical research focused on prevention rather than solely on treatment.
These advancements underscored a paradigm shift in healthcare:
-
From Treatment to Prevention: With tools like Tamoxifen, the medical community began to place greater emphasis on preventing diseases before they develop, which has far-reaching implications for public health strategies.
-
Inspiring Future Innovations: Tamoxifen’s success story inspired continued research into preventive medications for various cancers and other diseases, fostering an environment of innovation aimed at stopping illnesses before they start.
In summary, the medical and biotechnological breakthroughs of 1998, epitomized by the approval of Tamoxifen, have had a lasting impact on the approach to disease prevention and treatment. They paved the way for personalized medicine and continue to influence research and healthcare practices today.
8. Introduction of the Game Boy Color
In 1998, Nintendo made a significant leap in portable gaming with the release of the Game Boy Color (GBC). As the successor to the original Game Boy, the Game Boy Color maintained the beloved aspects of its predecessor while introducing new features that captivated gamers worldwide. The addition of a color display and enhanced hardware capabilities offered a more immersive and visually engaging experience, solidifying the Game Boy Color’s place in gaming history.
Advancements Over Its Predecessors
The Game Boy Color brought several key improvements to the handheld gaming market:
- Color TFT Screen: Replacing the monochrome screen of the original Game Boy, the Game Boy Color featured a color Thin Film Transistor (TFT) screen. This advancement allowed for more vibrant and detailed graphics, enhancing the visual appeal of games.
- Enhanced Processing Power: Equipped with a custom 8-bit processor made by Sharp that operated twice as fast as its predecessor, the Game Boy Color could handle more complex games and smoother gameplay.
- Increased Memory Capacity: With four times the memory of the original Game Boy, it supported larger games with more content, providing a richer gaming experience.
- Backward Compatibility: The Game Boy Color retained full compatibility with all original Game Boy games, ensuring that players could continue to enjoy their existing game libraries.
Impact on the Gaming Industry
The Game Boy Color’s release marked a significant moment in the fifth generation of video game consoles. Despite some reviewers questioning whether the upgrades justified a new product, gamers embraced the handheld enthusiastically. Its sales contributed to the combined total of over 118 million units sold worldwide for the Game Boy and Game Boy Color, making them the fourth best-selling system of all time.
Iconic games like Pokémon Gold and Silver found a home on the Game Boy Color, with these titles alone shipping 23 million units globally. The success of these games not only boosted the console’s popularity but also had a lasting influence on the gaming landscape, driving the continued success of the Pokémon franchise and handheld gaming.
Legacy of the Game Boy Color
The Game Boy Color’s blend of innovation and familiarity set a new standard for handheld consoles. Its ability to balance new features with compatibility honored the player’s investments in games and accessories. This approach solidified Nintendo’s reputation for customer-focused design and influenced future console developments.
Today, the Game Boy Color is remembered fondly by gamers and collectors alike. It represents a pivotal step in the evolution of portable gaming, bridging the gap between the original Game Boy and more advanced handheld systems. Its success demonstrated the market’s readiness for more sophisticated mobile gaming experiences, shaping the future of gaming on the go.
Conclusion
Reflecting on 1998’s innovations, we see their lasting influence on our everyday lives and technological landscape. These breakthroughs not only advanced their respective fields but also laid the groundwork for future developments. The creativity and ingenuity of that year continue to inspire us, reminding us of the power of innovation in shaping a better tomorrow. As we move forward, we remain grateful for these pioneering inventions that have seamlessly integrated into our modern world, enhancing how we communicate, entertain, and explore.